Fiber optic biosensor in biomedical Engineering
Fiber optic biosensor in biomedical Engineering
Fiber optic biosensors are a type of biosensor that uses optical fibers to detect and measure specific molecules in a sample. These biosensors are becoming increasingly popular due to their high sensitivity, specificity, and real-time capabilities.
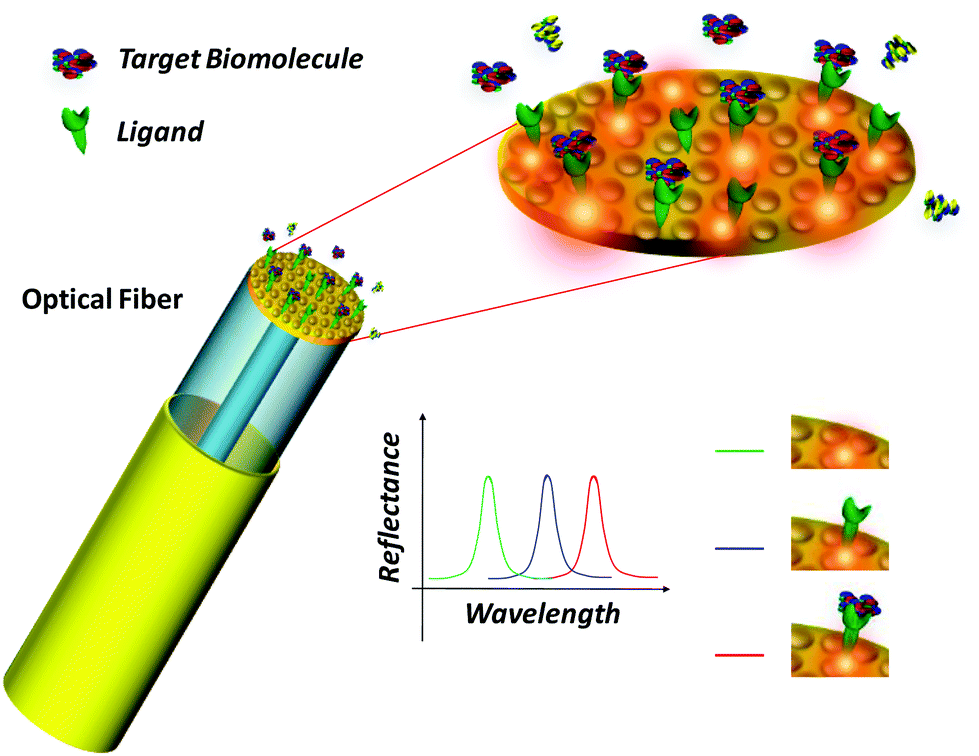
Fiber optic biosensors work by using the properties of light to detect and measure specific molecules in a sample. The core of the optical fiber is coated with a thin layer of a biological component, such as enzymes, antibodies, or DNA. When a sample is introduced to the biosensor, the biological component binds to specific molecules in the sample, and this binding causes a change in the properties of the light travelling through the optical fiber. This change in the properties of the light can be used to detect and measure the specific molecules in the sample.
Fiber optic biosensors have a number of advantages over traditional biosensors. They are highly sensitive, and can detect very low concentrations of specific molecules in a sample. They are also very specific, and can selectively detect and measure specific molecules in a sample, even in the presence of other molecules. Additionally, fiber optic biosensors can operate in real-time, allowing for continuous monitoring of specific molecules in a sample.
Fiber optic biosensors have a wide range of applications in medicine, such as in-vitro diagnostics, point-of-care testing, and continuous monitoring. They are also used in environmental monitoring, such as detecting pollutants in water and air, and in industrial processes, such as monitoring glucose levels in fermentation processes.
Fiber optic biosensors are also being integrated into portable and wearable devices, such as smart watches and fitness trackers, to allow for continuous monitoring of specific molecules in the body. This can help to improve human health by allowing for early detection and treatment of various diseases and conditions.
In conclusion, fiber optic biosensors are a type of biosensor that use optical fibers to detect and measure specific molecules in a sample. They are highly sensitive, specific, and can operate in real-time, and have a wide range of applications in medicine, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes. Additionally, with advancements in technology, fiber optic biosensors are increasingly being integrated into portable and wearable devices, which has the potential to greatly improve human health.

Comments
Post a Comment