CT or computed tomography explained
CT or computed tomography explained
Computed Tomography (CT) is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of internal organs, bones, and other tissues. CT scans are often used to diagnose diseases and injuries, and to monitor the progression of treatment.
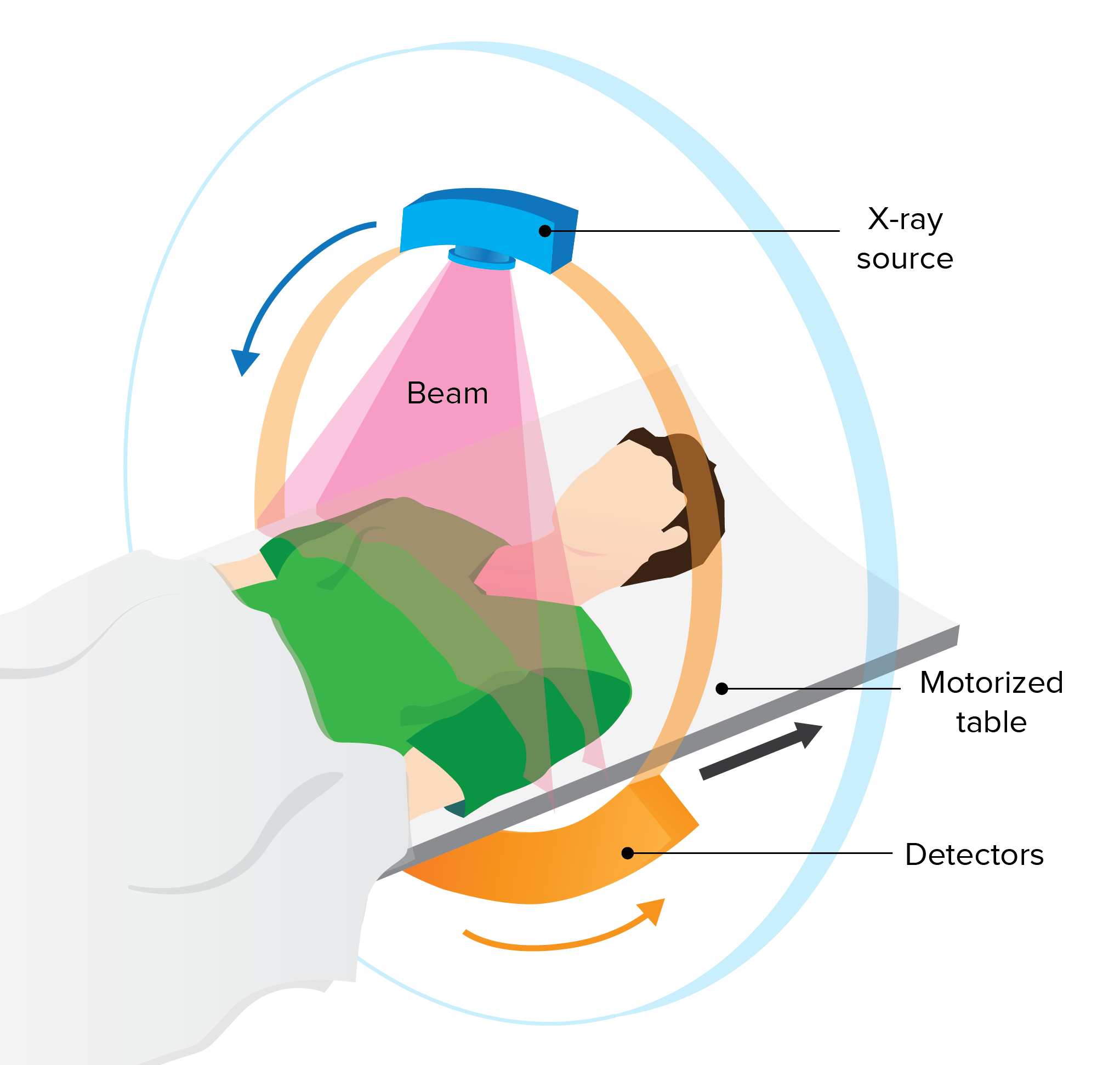
The basic concept of CT is to take a series of X-ray images from different angles around the body and then use a computer to combine them into a detailed 3D image. CT scans work by using X-ray beams to penetrate the body and create an image of the internal structures. The X-ray beam is emitted from a circular tube called an X-ray source and is directed at the body part being scanned. The X-ray beam passes through the body and is detected by an array of detectors on the opposite side.
The CT scanner takes multiple X-ray images, each at a slightly different angle, while the patient is moved through the machine. The computer then combines these images to create a detailed 3D image of the internal structures. The computer can also use mathematical algorithms to create cross-sectional images of the body, allowing doctors to see inside the body in much greater detail than conventional X-rays.
There are different types of CT scanners, including single-slice and multi-slice scanners. Single-slice CT scanners take one image at a time, while multi-slice CT scanners can take multiple images at once, allowing for faster scanning and more detailed images.
CT scans are widely used in many medical fields, including emergency medicine, neurology, oncology, and cardiology. It allows doctors to visualize internal structures, bones, blood vessels, and soft tissue in much greater detail than traditional X-rays, making it an important diagnostic tool. However, it should be used carefully and only when necessary, as it exposes the patient to ionizing radiation which may have negative effects in the long term if overused.
Comments
Post a Comment