Concept of Einthoven triangle explained
The Einthoven triangle is a concept in electrocardiography (ECG) that describes the location of the three leads (or electrodes) used to record the electrical activity of the heart. The Einthoven triangle is named after Willem Einthoven, the Dutch physician and physiologist who developed the ECG and the Einthoven triangle in the late 19th century.
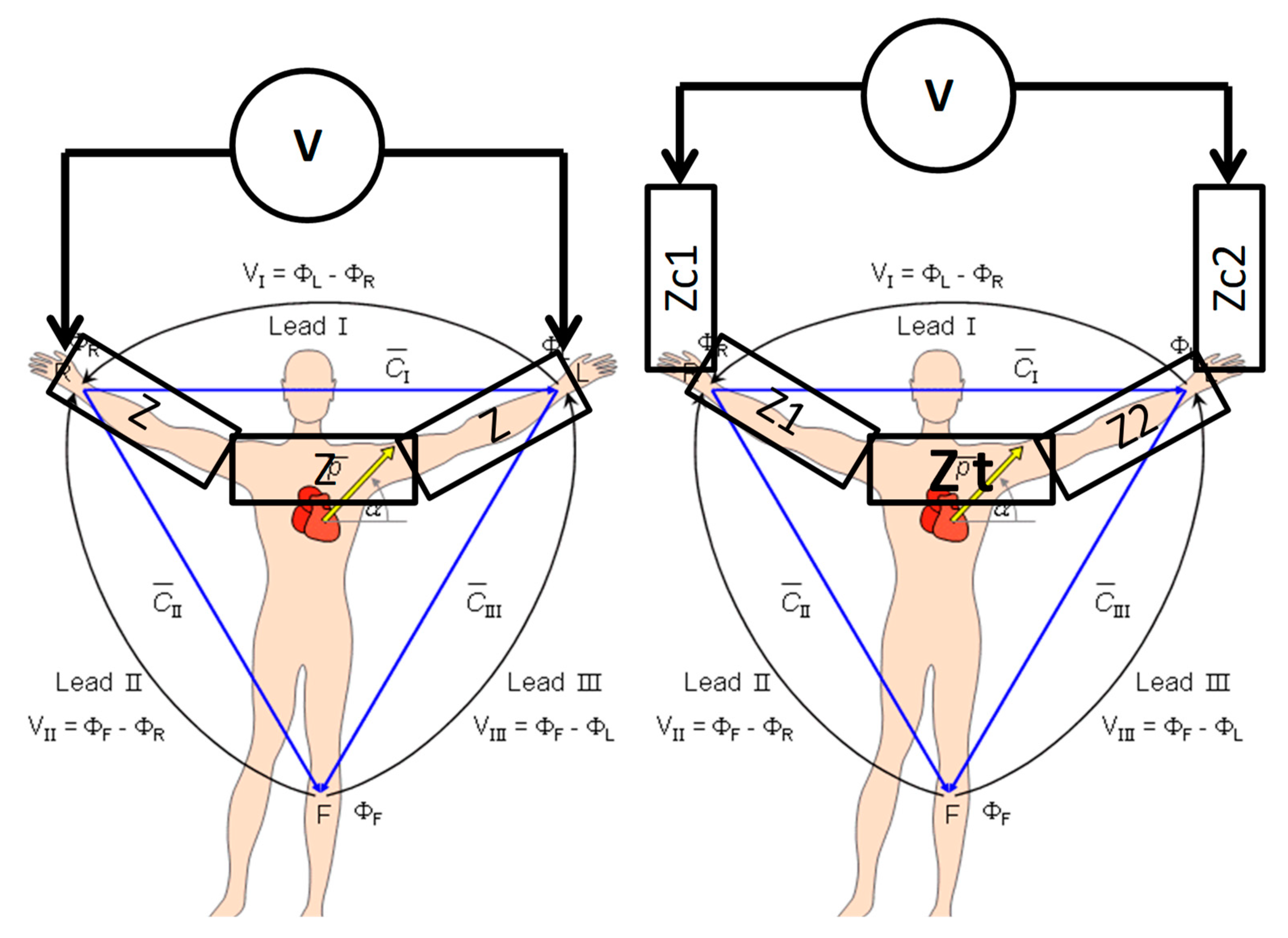
The Einthoven triangle is a theoretical representation of the heart and the location of the three leads. The three leads are positioned at the corners of the triangle and are used to record the electrical activity of the heart. The three leads are:
Lead I: This lead is positioned between the right arm (RA) and the left arm (LA) and records the electrical activity of the heart between the right arm and the left arm.
Lead II: This lead is positioned between the right arm and the left leg (LL) and records the electrical activity of the heart between the right arm and the left leg.
Lead III: This lead is positioned between the left arm and the left leg and records the electrical activity of the heart between the left arm and the left leg.
These three leads record the electrical activity of the heart at different angles and provide a complete picture of the heart's electrical activity. The Einthoven triangle is used to interpret the ECG tracing and to diagnose and evaluate conditions such as heart attacks, arrhythmias, and heart disease.
It's important to note that in modern electrocardiography, the use of 12 leads to record the electrical activity of the heart have been expanded, each one of them is placed on a different location on the body. This provides a more complete picture of the heart's electrical activity, and thus helps in identifying different types of problems or issues with the heart.
Comments
Post a Comment